Travel
UK Electronic Travel Authorisation: What is the new visa-free entry system?
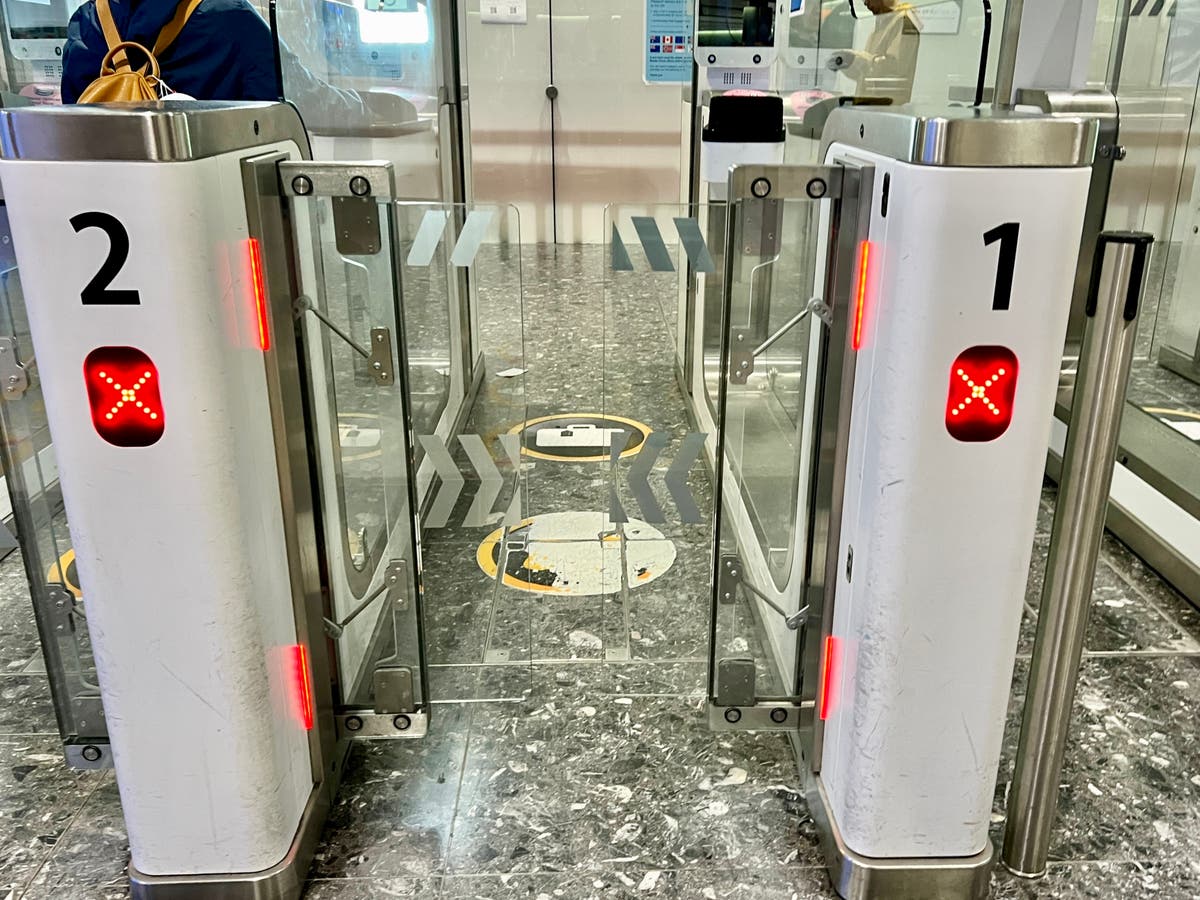

The UK’s Electronic Travel Authorisation (ETA) scheme is now in operation – but currently only for visitors from Bahrain, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the UAE. It costs £10 and is valid for two years, unless the traveller’s passport expires sooner.
The government describes the ETA as “a new requirement for people who do not need a visa to come to the UK”. It will be needed even for those who are “airside” at Heathrow for two hours between international flights.
Announced the plan in March 2023, the-then immigration minister, Robert Jenrick, said: “ETAs will enhance our border security by increasing our knowledge about those seeking to come to the UK and preventing the arrival of those who pose a threat. It will also improve travel for legitimate visitors.
“The cost of an ETA will be one of the best value in the world compared to similar international schemes. This small additional cost to visitors will enable us to bolster the security of the UK border and keep our communities safe.”
For British travellers, there should be no direct impact. But travel industry figures say rules attached to the ETA will disadvantage UK airlines and tourism, particularly to Northern Ireland.
These are the key questions and answers.
What is planned?
Most visitors to the UK do not need to go through the complex and expensive business of applying for a British visa; they simply turn up with their passport and apply for entry.
But that is all changing with a new online permit, the Electronic Travel Authorisation, The ETA will be mandatory for all “non-visa” overseas visitors to the UK – except for Irish people, who are allowed free movement under the Common Travel Agreement.
The starting point of the journey to the UK is not relevant – it is the traveller’s nationality that counts.
The ETA is loosely modelled on the US Esta and is electronically linked to the traveller’s passport. The cost is £10. The permit will be valid for repeated journeys within two years or until the passport expires, whichever is sooner.
When is it happening?
The roll-out began with Qatari nationals travelling to or via the UK on 15 November 2023. On 22 February 2024 the programme was extended to nationals of Bahrain, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
In 2023 the government said ETAs would be a requirement for all visitors who do not need a visa for short stays by the end of 2024. But the pledge to have the system fully in place this year has been quietly dropped.
The government now says: “Other nationalities do not need to apply yet and timings for when the scheme opens for them will be confirmed in due course.”
How do travellers obtain an ETA?
Online through a UK government website or via the app (search for UK ETA on the Apple app store or Google Play).
You need to supply a photograph and answer a set of questions. The government says: “This will ensure we have information on those seeking to come to the UK helping to prevent dangerous individuals, such as criminals, entering the UK.”
A decision on each case is expected “usually” within three days. In practice, existing similar schemes in the US, Canada and elsewhere deliver approval more quickly.
Commercial sites that are designed to tempt applicants to pay additional fees have already appeared, such as etauk.uk, which is based in Spain and has no connection with the UK government.
Who will check the ETA?
For the majority of travellers, airlines and ferry companies will be expected to verify the ETA status before the passenger boards a flight or ship to the UK.
Ferries from France to Dover, Eurostar trains to London and Eurotunnel shuttles to Folkestone have “juxtaposed controls” and UK Border Force staff will check the permit while the traveller is in Continental Europe.
On arrival, UK Border Force will check the ETA and ask supplementary questions before deciding whether or not to allow the traveller in. The government says: “An ETA does not guarantee entry to the UK.”
Non-Irish and British travellers from the Republic of Ireland to Northern Ireland will not face checks but are expected to have an ETA anyway.
What about transit passengers?
The UK government has decided to become an outlier by insisting that all connecting travellers must obtain an ETA. This will make London Heathrow airport a more challenging transit hub than the main continental European competitors, plus airports such as Istanbul and Dubai.
The almost-worldwide convention is that passengers who are connecting from one gate to another at a hub – not passing through passport control – need only meet the requirements for their final destination.
But when the ETA scheme takes full effect, all passengers except British and Irish nationals will need a permit – even if they are simply switching from one British Airways plane to another at Heathrow Terminal 5, or making a Star Alliance connection at Terminal 2.
Travel industry experts predict overseas travellers with a choice of routings will switch to other hubs to avoid extra red tape and cost – harming Heathrow and leading to a slump in customers for British Airways and Virgin Atlantic.
About 30 per cent of passengers at Heathrow are in transit.
Thomas Woldbye, chief executive of Heathrow, said: “It clearly reduces the competitiveness of the hub that we have built in Heathrow, which I think is critical to the UK.
“Honestly, I think it’s a mistake. I think that should be changed as fast as possible.”
Paul Charles, director of The PC Agency and former Virgin Atlantic communications director, said: “Taxing transit is tantamount to failure. If other airports offer free transit then they will pick up market share.
“Airports should be zones of ease, enabling seamless travel. This proposed tax needs removing.”
Rob Burgess, editor of the frequent flyer website Head for Points, says: “Why would anyone pay £40 for a family of four to get an ETA purely so they can transit in the UK on the way from, say, the US to Croatia? All of the other European hub carriers will be laughing as they pick up this business.”
What does the government say?
A spokesperson for the Home Office said: ”We are introducing an Electronic Travel Authorisation (ETA) scheme to enhance border security by increasing our knowledge about those seeking to come to the UK and preventing the arrival of those who pose a threat.
“Requiring transit passengers to obtain an ETA stops people who may use connecting flights to avoid gaining permission to travel to the UK. We are keeping this under review as we continue to roll out the scheme.”
Government online information about the new scheme says: “Requiring those transiting to obtain an ETA will stop transit being a future loophole for people to use to avoid needing an ETA. This is in line with the US Esta scheme.”
If I’m changing planes in the US I need an Esta…
There is a crucial difference: all passengers in transit through the United States are required to clear Customs & Border Protection and be legally admitted to the US. In theory they could decide, instead of transferring at Atlanta, Chicago or Houston, to stay in America for up to three months.
This policy does not apply at Heathrow (or elsewhere in Europe) for international-to-international journeys. UK Border Force will not check passengers on arrival at Heathrow if they are continuing their journey internationally.
Furthermore, few US airports rely on transit passengers for business in the way that Heathrow does.
Besides the potential financial damage to airlines and Heathrow airport, the government decision could also impact British passengers. A number of routes and frequencies are viable only because of the volume of connecting passengers. If services are cut, choice will reduce and fares could rise.
Any other objections?
Yes: from the inbound tourism industry, particularly in Northern Ireland. The UK has already excluded more than 200 million European Union citizens from entry by insisting they carry passports rather than their national ID cards. Bringing in an ETA will add one more hurdle.
There is special concern in Northern Ireland. Typically visitors to the island of Ireland will arrive in Dublin or, for some US travellers, Shannon. They enter the Republic and typically travel around by car, public transport or tour coach.
At present they can enter Northern Ireland without formality, to visit attractions such as Titanic Belfast, the Giant’s Causeway or the Game of Thrones studio tour. By the end of 2024 they will all legally require an ETA to cross the (almost invisible) border.
Individual tourists may inadvertently break the law by crossing the border and remaining blissfully unaware of their transgression.
But tour groups will follow the rules. Operators should ensure every passenger on the bus has an ETA. Or the tour firm may simply exclude Northern Ireland from Irish itineraries.
What could the effect be?
At present 60 per cent of non-UK tourists to Northern Ireland also visit the Republic, according to the Northern Ireland Tourism Alliance – which says the plan “will be hugely detrimental to tourism on the island”.
The group estimates visitors from Europe and North America could fall by 25 per cent. It says: “The risk is that many global tour operators will exclude Belfast and NI from their itineraries as no longer a feasible option.”
The government in London has confirmed that there will be no exemptions for tourists remaining solely within the island of Ireland.
In June 2023, the-then Northern Ireland minister, Steve Baker, said: “It is the government’s position that we should not create a loophole through the ETA scheme.
“I hope that we will be able to work together to ensure that there is a consistent and coherent communication strategy to ensure that tourists know they must register for an ETA and must continue to comply with the UK’s immigration requirements.”